Maintaining healthcare compliances is quite critical. Here’s exactly why. In February 2024 alone, 10,000 healthcare records were breached 24 times, the largest of which was a 2.35 million data record. These are likely to increase further since cybercriminals are exploiting the fact that organizations migrate to cloud without establishing strong data privacy policies. The stats speak for themselves here. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Office for Civil Rights (OCR) saw a 264% surge in ransomware incidents in the last 5 years as of 2024. These compelling figures make it of utmost importance to comply with industry laws and regulations.
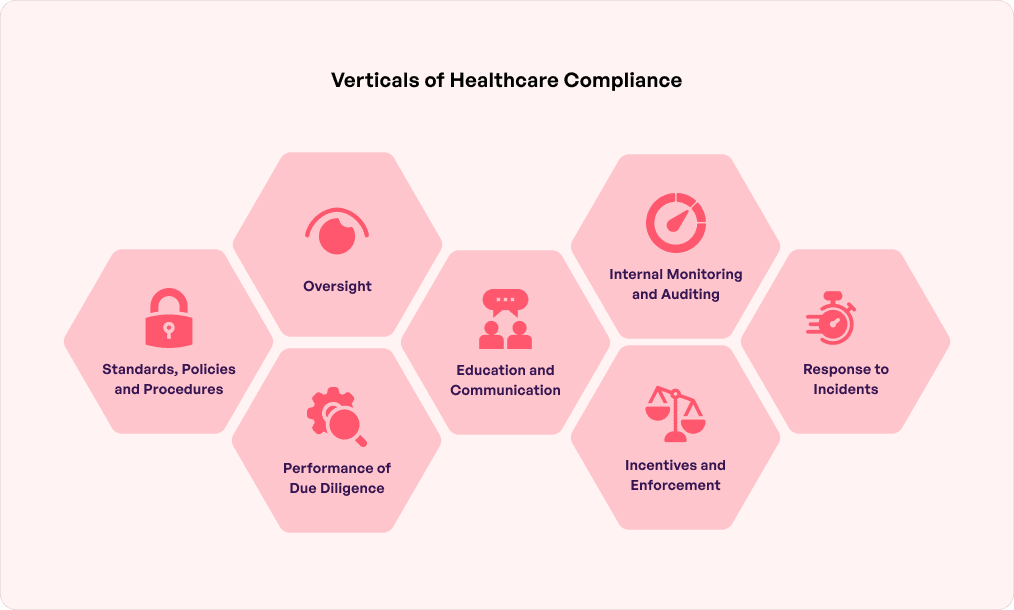
Healthcare is one of the most heavily regulated industries in the world. Compliance with relevant guidelines, laws, and ethical standards is a growing field within it. It helps ensure fraud protection, and risk mitigation and thus offers the best care to patients. Digital healthcare compliance is in terms of:
- Patient safety
- Patient privacy
- Physician and patient billing
- Data protection.
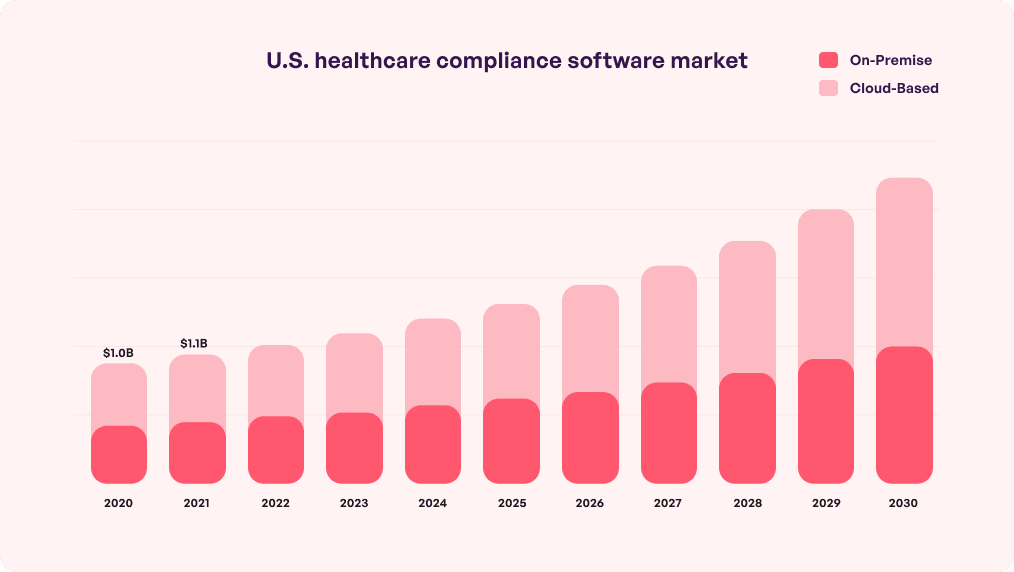 When it comes to data protection, medical institutions and healthcare professionals must be up-to-date with the specific regulatory compliance in healthcare apps. For instance, it must be HIPAA compliant which mandates robust security systems to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. The compliance also helps prevent identity theft, operations disruptions, and, thus serious reputational damage.
When it comes to data protection, medical institutions and healthcare professionals must be up-to-date with the specific regulatory compliance in healthcare apps. For instance, it must be HIPAA compliant which mandates robust security systems to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. The compliance also helps prevent identity theft, operations disruptions, and, thus serious reputational damage.
At Simublade, we carry exceptional knowledge in creating impactful healthcare apps. Enterprises trust us for our proficiency in building powerful EHR/EMR solutions. Our software development service are built in a way that connects doctors and patients in a secure virtual space while ensuring that we build a system that keeps recordkeeping and data sharing safe and compliant for clinics, and hospitals. Using AI, blockchain and similar next-gen tech is the USP of our healthcare app development company.
Table of contents
Top examples of healthcare compliance in detail
Strict adherence to healthcare regulations and compliance is not just a legal need but also a moral obligation. Further, the financial health of medical organizations and compliance are also directly connected. For instance, compliance will mitigate the risks of denied reimbursement claims, penalties, and loss of accreditation which otherwise impact revenue.
The profit pool of the healthcare industry is expected to reach $819 billion in 2027. Using compliance programs at grassroot level can help turn this estimate into reality. To help you get started, here is a checklist and an idea of the importance of regulatory compliance in healthcare.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
What is HIPAA compliance in healthcare? Well, this federal law was introduced back in 1966 with a purpose to protect sensitive and identifiable patient health information. It includes:
- Securing electronic records accurately.
- Offering detailed instructions about transmitting patient data.
- Simplifying administration and insurance portability.
All hospitals, pharmacies, nursing homes, clinics, healthcare clearinghouses, and individual practitioners like doctors, and issuers of Medicare supplemental policies, handling information electronically are covered entities of HIPAA. Further, any business associate involved in creating, maintaining, receiving, or transmitting Protected Health Information (PHI) must adhere to the healthcare regulations and compliance of HIPAA.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
At its core, GDPR compliance in healthcare originated from the European Union and now applies to EU citizens across the globe. This makes it stronger than local laws since it prevents data from traveling via channels that transcend geographical boundaries.
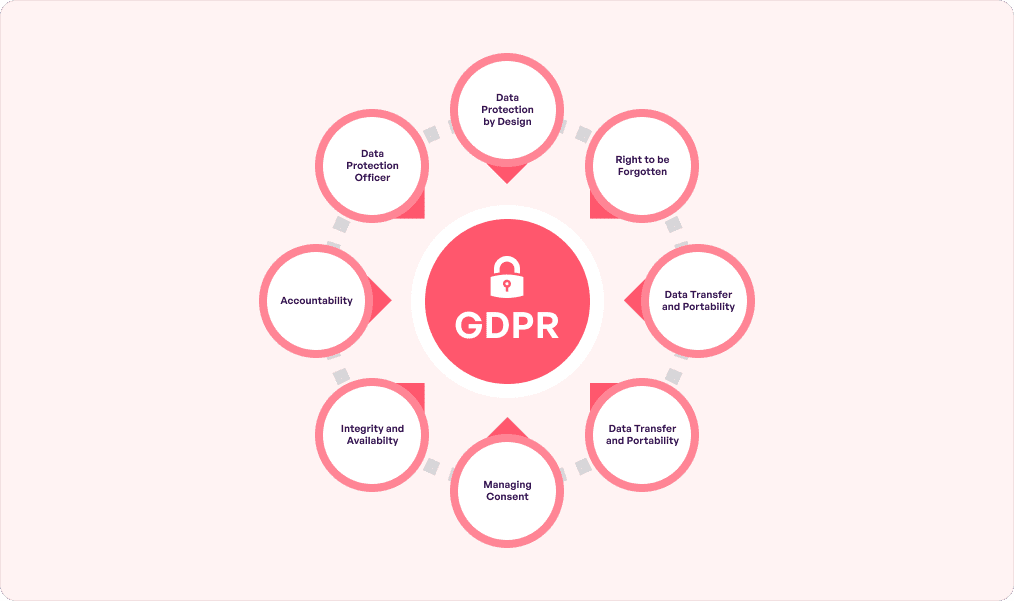 No wonder GDPR has emerged as one of the leading frameworks for individuals’ privacy protection. It especially applies to healthcare apps since they are treasure troves of confidential information. GDPR outlines strict policies for them in terms of collecting, processing, and securing 3 specific personal data types:
No wonder GDPR has emerged as one of the leading frameworks for individuals’ privacy protection. It especially applies to healthcare apps since they are treasure troves of confidential information. GDPR outlines strict policies for them in terms of collecting, processing, and securing 3 specific personal data types:
- Health data
- Genetic data
- Biometric data
These come under the ‘sensitive personal data’ category and require consent before being used in any form. Indirectly, GDPR is also a type of healthcare cybersecurity compliance which is critical since cybercriminals typically target the healthcare sector. Know that Article 33 under GDPR has a 72 hour window for reporting breaches to the concerned authority.
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH Act)
President Obama signed HITECH into law in February 2009. Since then, HITECH and HIPAA have merged and healthcare providers are required to comply with both as a single legislation piece. Altogether, it has motivated organizations to switch to electronic health records from paper ones with them getting benefitted in the form of high-end care coordination, proper engagement of caregivers and patients, and lower costs in the healthcare budget. Other perks included better tracking and access to patient information which ultimately boosts efficiency.
HITECH is responsible for handling security and privacy concerns associated with this electronic transmission of health data. This was an initiative to support technology growth in the USA. HITECH has also introduced the Breach Notification Rule where the covered entities can send a breach notification to patients within 60 days of data exposure. It should include:
- The nature of the breach that took place.
- The Protected Health Information that was compromised.
The US Department of Health and Human Services had received approximately $25 million to expand healthcare services as a part of HITECH. The fund was to expand primary healthcare services, even mental health related issues, in schools.
Health Level 7 (HL7)
HL7 is an international body with a set framework of standards. It defines high-end secure methods to transmit, integrate, share and retrieve electronic health data. Proper messaging standards, clinical/administrative data, and data formats are in place to enable consistent data exchange. In short, HL7 aims to ‘achieve interoperability in healthcare.’
This is made possible with stringent encryption techniques and protocols that help maintain confidentiality. So, this eliminates the risks of a breach while swapping sensitive patient data. The standards evolve from time to time and strive to integrate the latest technologies. This boosts efficiency in several environments of the healthcare landscape.
Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
This is the gold standard when it comes to the safety, quality, and effectiveness of a medicine. Compliance with this agency within HHS means adhering to public health protection. This includes regulating vaccines, human and vet drugs, dietary supplements, medical devices, tobacco products, electronic radiation-emitting devices, and cosmetics.
To get approval from the FDA, a pharmaceutical company selling prescription drugs must follow a few steps:
- Discovery/Concept: Drugs should undergo both animal testing and human trials to check their efficacy.
- Pre-Clinical Research: A New Drug Application (NDA) should be sent to the FDA. This includes data gathered from the above-mentioned test result.
- FDA Review: The scientists will review the drugs, usage instructions, and information labels. The product will be approved if the benefits surpass the risks. The pharmacy can then market it in the US.
- Post-Market Safety Monitoring: The FDA will continue to monitor the drug even after approval.
Manufacturers of over-the-counter drugs and generic drugs must also be compliant with FDA rules and regulations. In all, this regulatory compliance in healthcare helps speed up innovations and help the public receive accurate and science-based information.
21st Century Cures Act
This act was introduced to speed up the start of clinical trials and bring new innovations by easing administrative burdens. To do that, it offers resources and tools to advance end-to-end biomedical research. This includes basic foundational research studies to advanced clinical trials. The Cures Act also implements measures to improve privacy for research volunteers and encourage clinical research on a diverse population.
Besides this, the act made electronic health information sharing an expected norm in the healthcare industry. Further, the Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS) has also been permitted to identify ‘reasonable and necessary activities that do not constitute information blocking.’ The law has been applied to health information networks, health IT developers, and healthcare providers in general.
The Purpose of adhering to health compliances
Compliance ensures healthcare organizations and caregivers offer and maintain the highest care procedure and standards. Adhering to them means meeting legal, ethical, and professional standards to ensure smooth operations in the healthcare industry.
- Conducting regular billing audits: This ensures all bills, claims, and coding of physicians and patients are aligned with ethical and accurate regulatory needs.
- Precise claims documentation: Healthcare organizations should adopt a claims compliance program with documented guidelines and procedures. It must comply with state and federal policies. Proper staff, trained and educated, must be present to manage the claims process as this would help minimize the risks of fraud.
- Patient safety and privacy: Hospitals, clinics, nursing homes, and health workers must set particular standards of well-being for patients. Organizations should also implement stringent privacy and data security measures to prevent the leakage of sensitive information into the wrong hands.
Consequences of compliance violation
Non-compliance to digital healthcare compliance like HIPAA, HL7 and HITECH, can lead to criminal penalties. This will depend on the severity of the case. Healthcare organizations might face criminal charges in case they have violated deliberately and repeatedly. You might end up paying $100-$50,000 per civil violation. The guilty might also be referred to the Department of Justice and subjected to imprisonment for up to 1 year.
Penalties can escalate to a serious written warning, contract termination, and suspension of services. Further, Medicare participation might be canceled for covered entities that do not comply with the compliances that apply to them.
These solid penalties are in place since even the smallest violation can impact patient care, lead to identity theft and destroy their relationship with medical institutions forever.
Simple strategies to prevent compliance violation
Health professionals can maintain the trust of the public and avoid legal repercussions by following these simple steps:
- Compliance rules are constantly evolving and complex layers are being added to them. Organizations must stay updated and educated to be able to address the changing needs with the latest knowledge.
- Ongoing training of the entire staff must be prioritized and regularized. Increasing the scrutiny at each step is an effective way to never violate compliance.
- Ensure open communication with the compliance officer for continuous improvement, implementation, and maintaining laws while identifying risks.
- Higher focus on privacy and information security with encryption to avoid breaches. This can be done by restricting access to health applications and information, eliminating connected-device risks, and conducting risk assessments daily.
A future-ready software is the smartest way to stay compliant. At Simublade, we offer exactly this. Our healthcare app development process includes aligning with industry-level standards to build HIPAA compliant health apps and similar ones. We dive into the core processes being followed by clinics, hospitals, doctors, and nurses and build a truly valuable solution. In return, you enjoy lower costs and better outcomes.
FAQs
Q. What is healthcare regulatory compliance?
Ans. Healthcare compliance means adhering to regulations, guidelines, and laws to run the healthcare industry without compromising on quality care.
Q. What are the benefits of a compliance program in healthcare?
Ans.
- Higher patient care and safety.
- Improved operational efficiency.
- The best use of available tools and resources.
- Continuous transparency in all verticals.
- Reduced risks of violations and thus repercussions.